
Many infections do not cause symptoms in healthy people. The immune system, inhibits the activity of the virus, causing the man becomes a carrier of infection. When the transmission of the pathogen to other people happens also to full clinical well-being, as the viral particles contained in the biological fluids of the patient. Hidden during the infection can be the root cause of a significant spread of the disease: the patients were not promptly submitted to the survey and continue to infect other people irresponsible.
The human papilloma virus (HPV) can be defined as a good example of hidden the infectious agent. Most of the people is infected with at least one type of HPV during the course of life, but the clinical manifestations of the disease occur in all cases. As far as complications of the infection, the doctors report an increase in the risk of the formation of a malignant tumor. In this case the patients suffering from human immunodeficiency, there is often a negative consequence of the disease. Topical medications help to suppress the symptoms of the HPV infection. We also recommend the vaccination in a timely manner.
Read more about the disease
The human papilloma virus is the causative agent of infections, that affects the skin and mucous membranes of the organs. The main manifestation of the disease is the growth of tumors in the area of the face, the genitals, the mouth and throat. In some cases, pointed papilloma virus are formed in non-specific places, like the skin of the upper and lower limbs. Localization of warts depends on the type of HPV. Most people, the infection leads to hidden transport infection, however, when immunity the virus starts to show its virulence. In some cases, of the immune cells to destroy the pathogen for 3-6 months after its invasion in the body.
The HPV infection is the most common sexually transmitted disease. This indicator may explain the high virulence of the virus and asymptomatic malocclusions with most people. The use of a condom does not always allow to avoid the infection, so the patient can continue to spread the virus even if protected by from sexual contact. At the same time, experts have developed effective vaccines that prevent the development and oncogenic forms of HPV. Immunization shows the girls as teenagers, because the virus protection, it is necessary to infuse at the first sexual contact.
Characteristics of the virus
The human papilloma virus is a DNA containing a pathogen. Unlike bacteria and other micro-organisms, viruses can exert their activity only after the introduction into the cell, and embedding of a genetic information in the nucleus. After this impressive the cell begins to synthesize the protein necessary for the assembly of viral particles. Almost all the representatives of the human family, attacking only one type of organisms, and HPV infection can occur is for one person only.
Scientists know more than 600 strains (types) of the human papilloma virus, which differ in genetic information. 40 types of HPV cause different forms of lesions of the mucous membranes and skin. With this important clinical value has the classification of the degree of oncogenetic strains. So, cancer of the neck of the uterus in women occurs most often during the invasion of HPV 16 and 18 types. These infectious agents do not always manifest skin changes.
HPV affects the basal layer of the epithelium. The pathogen can exist in the form of the episoma, not tied to the cell's DNA, or an integrated form, connected with the genome of the cells. Is integrated in the virus produces the necessary proteins and causes the clinical manifestations of the disease. The vital functions of HPV in the body is not the direct cause of malignant transformation of the tissues, but carriers of the virus increases the risk of cancer risk factors.
Methods of infection
The virus content in the basal cells of the epithelium, and therefore any microtrauma of the skin and of the mucous membranes increase the risk of infection. In most cases, HPV is transmitted vaginal, anal or oral through sexual contact. The condom can protect only the superficial part of the skin, however, the viral particles can penetrate the body through the other dishes. The presence of genital warts predispose to the transmission of the pathogen, but the exterior of the skin intact, the carrier of the disease is also a source of HPV.
Other routes of transmission
- The infection of the child during birth. Children often occur lesions of the respiratory tract
- Self-transfer of the virus from one area of the body to another
- The common use of objects for personal hygiene, including razors, toothbrushes and towels
- A blood transfusion. Recent studies have confirmed the possibility of transfusion-related infection.
- Surgical interventions in hazardous conditions
Despite the variety of causes of a virus infestation, only sexual route of infection with HPV has clinical significance. Other sources of infection are characterized by a low risk of spread of the pathogen.
The risk factors
Beyond the immediate ways of transmission of HPV, you must also consider the role of risk factors. It is characteristics of the style of life of man and of some physical states.
The key risk factors of infection
- A large number of sexual partners. Even during safe sex an active sex life, sooner or later, leads to infections.
- Age. Genital warts in the majority of cases reported in adolescents and young patients, while sharp in the oral cavity and respiratory tract are characteristic for children.
- A weakened immune system. Patients suffering from HIV infection or acquired immunodeficiency, are at high risk of viral invasion. Also, HPV most often manifests itself symptomatic after transplantation.
- The damage of the skin and mucous membranes. Microtrauma facilitate the penetration of the virus into the basal layer of the epithelium.
- Smoking and alcoholism. Bad habits relax the activity of the immune system.
- Urinary tract infection.
Furthermore, in a group at risk of infection include pregnant women. It must be remembered that the removal of the factors of predisposition to the disease is an effective preventive tactic.
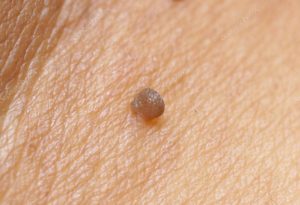
Clinical course
The incubation period, which precedes the symptomatic manifestations of the disease, may last for months or not. In immunocompetent patients during this time, the body can destroy the infection, however, spontaneous elimination of the pathogen is not always the case. Man can be infected with different strains of the virus. Signs of HPV infection occur when the impact of unfavorable factors, can weaken the immune defences of the tissues. Because of the recurring flow of condyloma periodically disappear and form again. The complications infections may develop in a few tens of years.
The possible consequences of the disease:
- Cancer of the neck of the uterus – the outgrowth of malignant epithelial tissue. This type of oncology for the most part only with the human papilloma virus. During the early vaccination risk of oncogenesis is reduced.
- Squamous anal cancer. This complication can occur in both men and women. The early symptoms of cancer of the anus include bleeding and itching of the skin.
- Violation of urination due to obstruction of the urethra warts.
- Malignant transformation of warts in the throat area and oral cavity.
Cervical cancer is one of the most frequent causes of death for women. Since this disease is associated with virus invasion induced, it is necessary to regulate the transfer of investigations to the gynecologist. Modern vaccines protect women against more types of HPV oncogenic.
Diagnostics
The examination of warts, deal with gynecologists, urologists, venerologia, and dermatologists. During the first reception the doctor asks the patient about the complaints, it will collect the history data, and by means of formations on the skin. Usually, the manifestations of HPV infection are easily identifiable, however, it is necessary to exclude other diseases. This specialist will prescribe the instrumental and laboratory.
Methods of diagnosis:
- Ow inspection of the vagina and cervix (colposcopy). This research necessarily takes place for screening of cervical cancer. During the examination, the doctor can locate multiple papillomas, and areas of epithelial dysplasia.
- Biopsy – to obtain material of the fabric in the area of the skin or of the mucous membranes of the changes. The cytology of the sample allows us to identify the malignant cells.
- Polymerase chain reaction – detection of viral particles of HPV in the body. The performance of this test gives the doctor the opportunity to identify the pathogenic strain and the viral load.
- Digene-test – accurate identification of the DNA oncogenic strains of the human papilloma virus. The research is used as a reliable selection.
Pharmacological treatment
Developed drugs against HPV infection, they only help to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and to prevent malignancy tissues. Complete elimination of the virus with the help of drug therapy is not possible. Oral and topical funds assigned to the case of high risk of oncogenesis, immunodeficiency, and other adverse events to the state. If the virus does not manifest external changes, quite common prevention measures.
The possible destinations
- Salicylic acid for the removal of warts. It is not used for the treatment of the skin of the face and genitals.
- Creams and ointments containing immunomodulators funds.
- Podofilox – ointment, possess cytostatic effect. The application of the drugs on the affected skin leads to the destruction of pathogens.
- Trichloroacetic acid for cauterization general chemistry, and genital warts. Can cause the local expression section.
Listed medicines must be used only under a doctor's supervision. After the removal of HPV warts the infection may occur again and also spread to other areas.
The surgical treatment
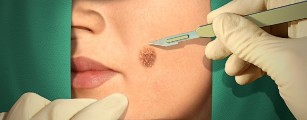
The doctor may suggest the surgical patient and minimally invasive methods of removal of warts. Usually these methods do not cause complications, however, in the first days after surgery may occur bleeding of the tissues.
Types of intervention:
- normal surgical excision;
- freezing with liquid nitrogen, resulting in destruction of the tissues;
- electric coagulation;
- removal of warts with laser.;
- the use of radio waves by the knife.
All treatments are performed under local anesthesia. Specialist to select the most safe method for the treatment of warts.
Forecast
For human papillomavirus infection depends on the immune status of the patient and a particular strain of the virus. In about 30% of the population is born spontaneously the elimination of the pathogen of the disease, due to active immunity. Symptomatic the disease often occurs in pregnant women, children, the elderly, and patients with immunodeficiency.
The HPV infection is a typical relapsing within. The warts may gradually disappear or spread to the adjacent areas of the skin. Oncogenic strains of the virus often affect the mucous membrane of the neck of the uterus, and occurs tumor epithelial dysplasia increases the effect of the risk factors of malignant transformation of the tissues, such as the smoking and use of oral contraceptives. The tumor may form after 10-20 years after the invasion of the virus in the body.
Prevention
The most reliable method of prevention is immunization. The vaccine "Gardasil", which contains viral proteins and components of the auxiliary, which is effective against HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18 types. If the vaccination is carried out at an early age at first sexual intercourse, the risk of later development of cancer of the neck of the uterus in women does not exceed 1%.
More prevention:
- the use of a condom;
- sexual relations only with reliable partners;
- careful personal hygiene;
- gynecological examination at least once a year.























